Matrix Formulation Of Electromagnetic Scattering
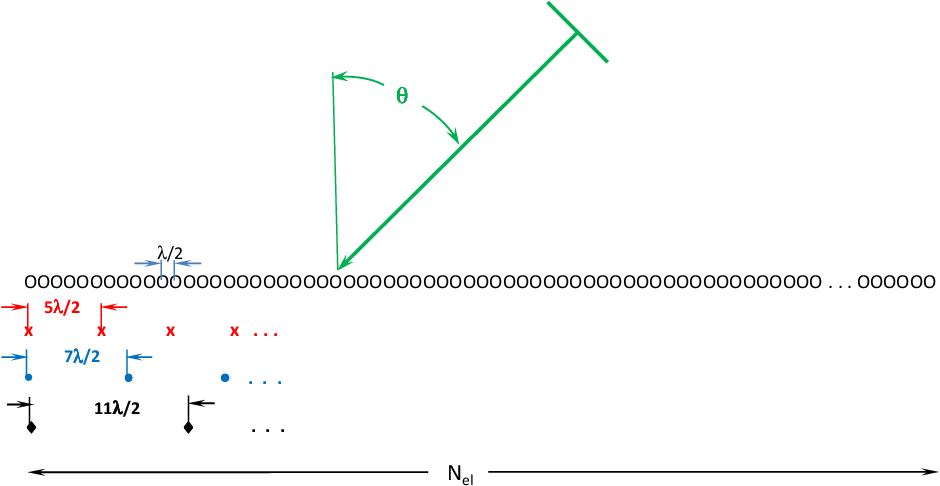
The scattering of electromagnetic waves from 2d surfaces.
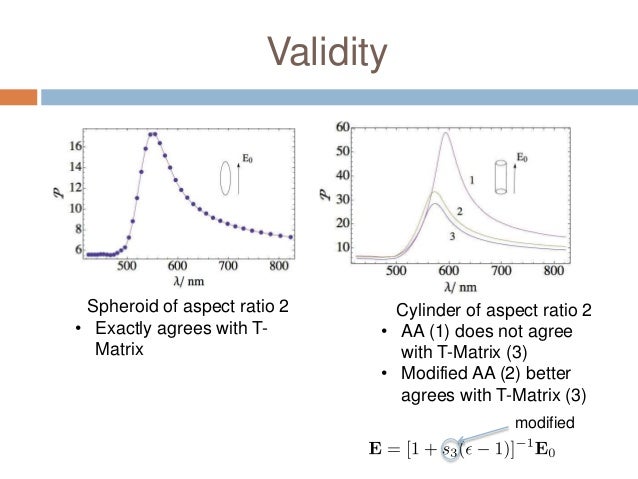
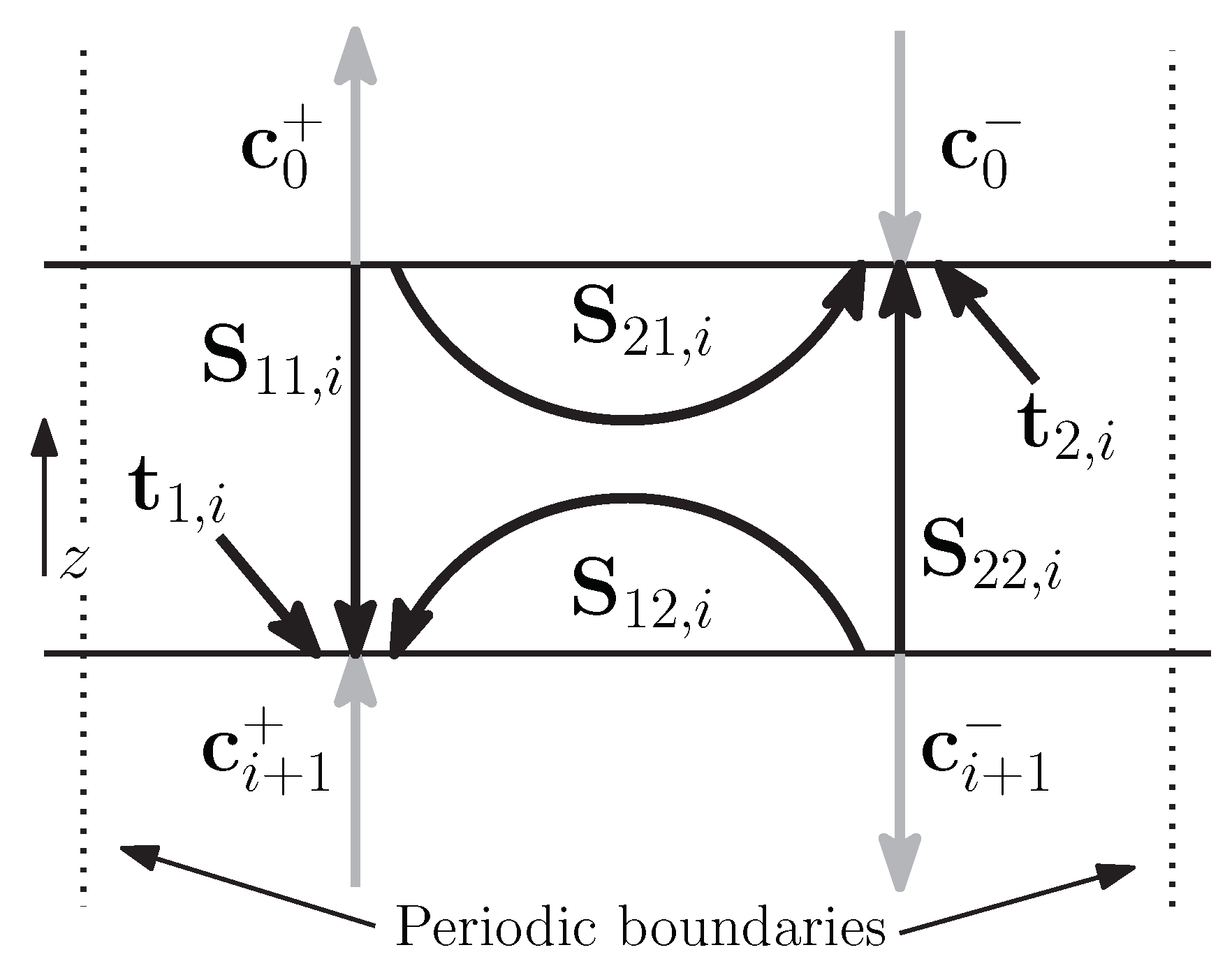
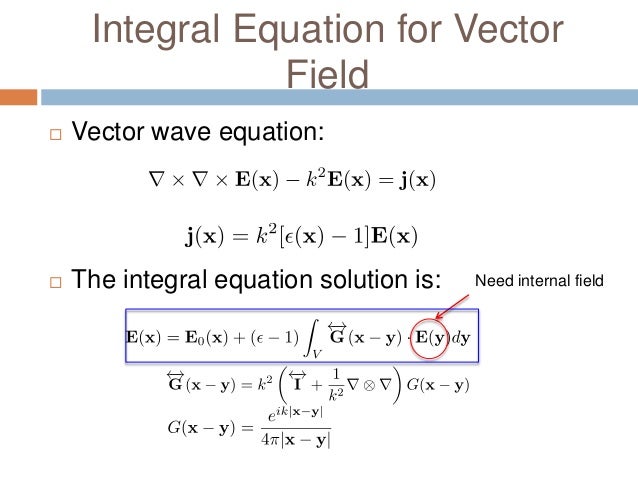
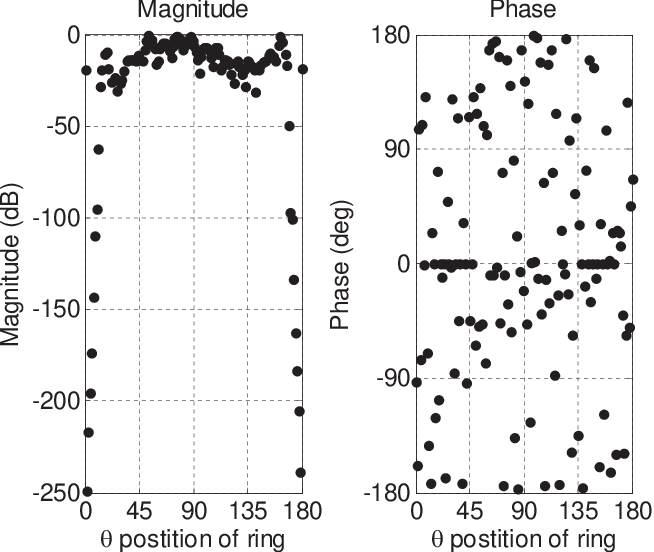
Matrix formulation of electromagnetic scattering. This work presents the clifford cauchy dirac ccd technique for solving problems involving the scattering of electromagnetic radiation from materials of all kinds. Thus when the surface charge density of the scatterer is given we can calculate the scattering field by using the transition matrix t c matrix between the coefficients of scattering field and incident field. The scattered wave is first represented by a distribution of electric dipoles over the surface in question with the response from any dipole proportional to the induced surface current density at that point.
In the method matrix elements are obtained by matching boundary conditions for solutions of maxwell equations. Outline 1 motivation 2 scattering system 3 problem formulation 4 the stratton chu formula and related equations 5 numerical results perfect conductors metals via the impedance boundary condition 6 conclusions 2 ingve simonsen et al. A secondary objective is to present some recent andsomenew theoretical results basedon this theory.
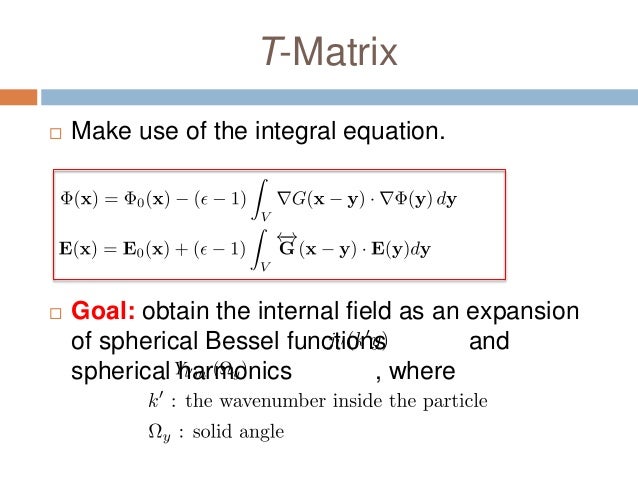
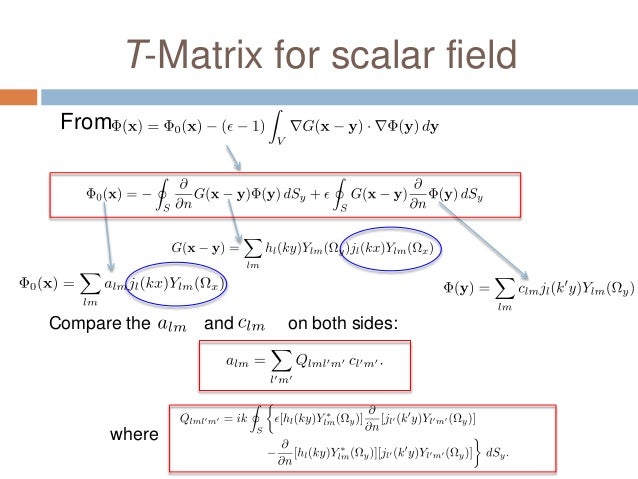
Based on watermans extended boundary method a transition matrix between coefficient of the scattering field and incident field of a charged non spherical scatterer is derived called t c matrix. The technique is also known as null field method and extended boundary technique method ebcm. The t matrix method is a computational technique of light scattering by nonspherical particles originally formulated by peter c.
Recently a t matrix formulation of classical electromagnetic scattering has been given by waterman for the case of one homogeneous scattere and this formulation has subsequently been extended to the case of an arbitrary number of homogeneous scatterers by the present authors. 11 scalar wave scattering 270 111 formulation and numerical method 270 112 results and discussion 273 113 convergence of smfsia 277 12 electromagnetic wave scattering by perfectly conducting surfaces 278 121 surface integral equation 278 122 surface integral equation for rough surface scattering 280 123 computation methods 281. Matrix formulation of electromagnetic scattering.
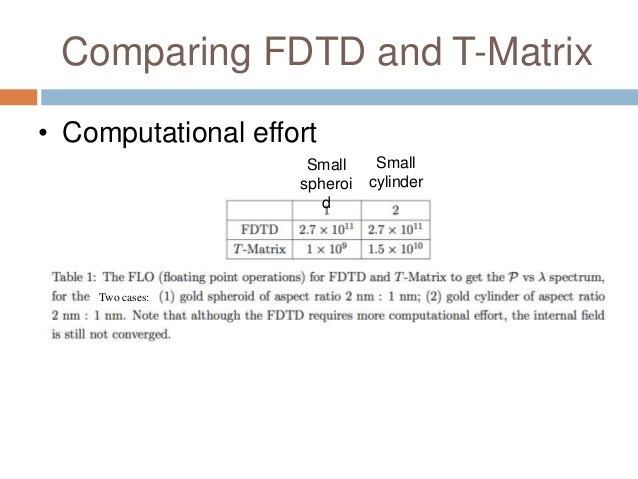
Abstracta new method is proposed for the computation of the radar cross section and other associated field quantities arising when a smooth perfectly conducting obstacle is illuminated by an incident electromagnetic wave. That means we can obtain the scattering field of a charged scatterer of any shape.